Aging is a natural process that can lead to various physical changes, especially in muscle mass and strength. Though it’s common to experience a decline in muscle as we age, these changes are not entirely irreversible. Understanding the essential strategies for preserving muscle mass can empower you to maintain strength and vitality throughout the years. Here’s a closer look at some key components to effectively maintain muscle mass as you age.
The Importance of Strength Training
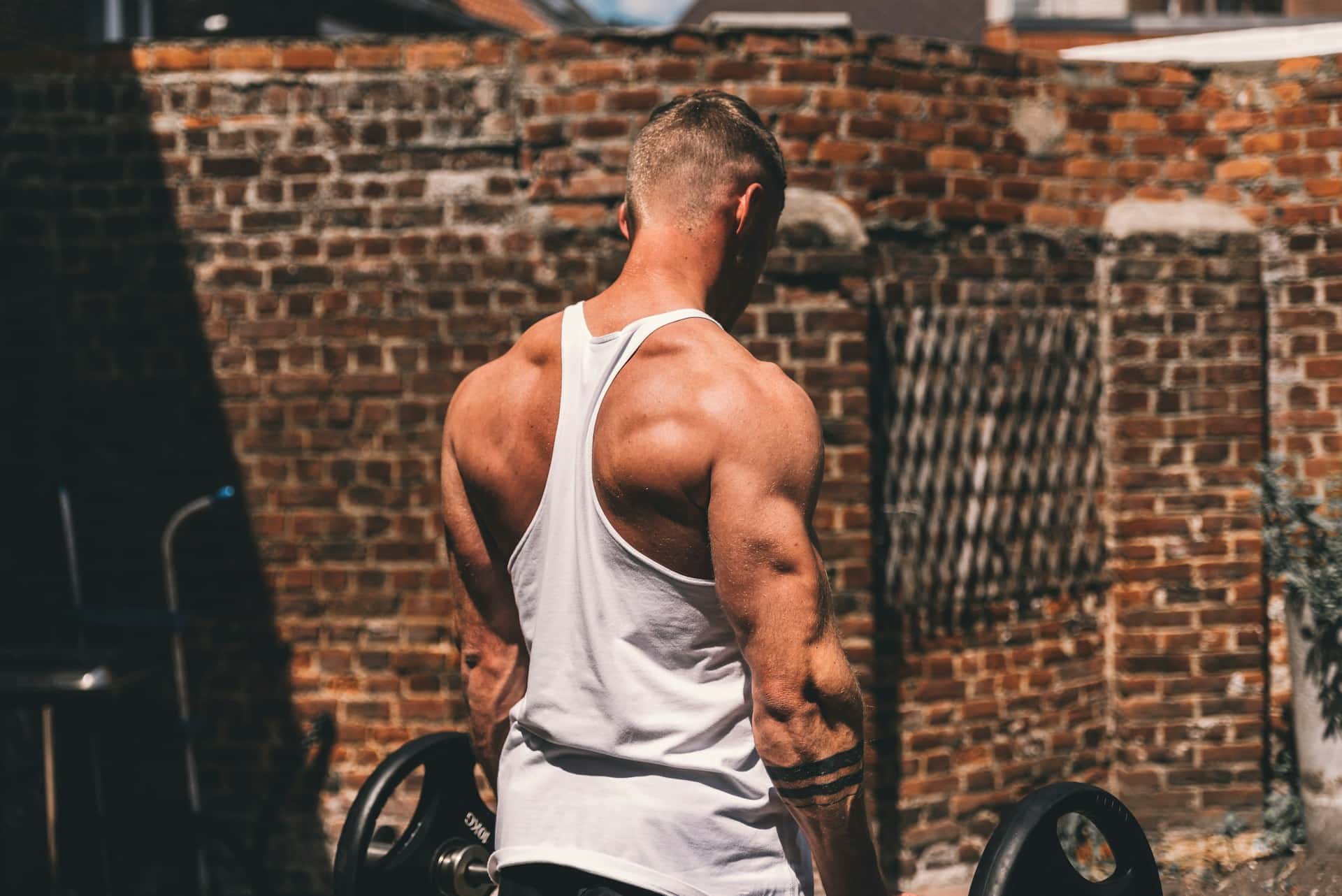
To combat muscle loss due to sarcopenia, strength training should be at the forefront of your exercise regime. Engaging in resistance exercises—whether it’s weightlifting, bodyweight workouts, or lighter resistance routines—stimulates your muscle fibers and signals your body to retain strength. Aim for two to three full-body sessions each week, focusing on compound movements (like squats and deadlifts) alongside smaller accessory exercises. Consistency is paramount; sporadic training can result in losing the gains you’ve made.
Fuel Your Muscles with Quality Protein
A well-rounded diet is crucial for muscle maintenance, particularly adequate protein intake. As we age, the body’s anabolic resistance increases, making it less effective at utilizing protein. This means you should strive for higher-quality protein sources such as lean meats, fish, eggs, and dairy products. Distributing your protein intake throughout the day maximizes absorption and aids in muscle synthesis. When coupled with strength training, a protein-rich diet can significantly enhance your results.
Integrate Cardio into Your Routine
Cardiovascular activity shouldn’t be overlooked in muscle preservation strategies. Cardio helps enhance circulation, heart health, and endurance—all of which are beneficial during strength training. If you’re concerned about joint wear or pain, consider low-impact options like cycling, swimming, or brisk walking. A balanced exercise routine that combines both strength training and cardio not only aids muscle retention but also promotes overall fitness and joint health as you age.
Hormonal Balance Matters
As we age, hormonal changes, particularly a decline in testosterone levels, can impede muscle repair and overall vitality. Addressing hormone balance through lifestyle choices—like stress management and adequate sleep—can improve muscle maintenance. For some, supplements might provide a more direct solution. Prioritizing hormonal balance creates a supportive environment conducive to muscle retention, further enhancing your training efforts.
Don’t Neglect Mobility
Alongside strength training and cardio, mobility exercises hold significant importance. As we age, reduced flexibility and range of motion can lead to stiffness and increased injury risk. Incorporating mobility workouts, stretching, and flexibility training can enhance your overall movement quality. Activities such as yoga and Pilates not only improve posture but also facilitate proper form during resistance training, ultimately contributing to long-term strength retention.
Prioritize Recovery and Rest
Recovery is a vital component of muscle maintenance that often takes on greater importance with age. Muscles typically require more time to repair, and inadequate recovery may lead to injuries. Ensuring 7-9 hours of quality sleep allows your body to repair tissues and release essential hormones. Active recovery through light exercise can enhance the recovery process, but always listen to your body’s signals to find the right balance.
Consistency is Key
While sporadic bursts of motivation can inspire short-term commitment, long-term muscle maintenance hinges on consistent habits. Neglecting workouts, poor nutrition, or inadequate sleep can quickly lead to muscle loss. Establishing a balanced routine—complete with planned workouts, nutritious meals, and mindful recovery—will support sustained progress. A holistic approach to your lifestyle, involving social interaction and stress reduction, further enhances your overall quality of life.
Although the effects of aging are inevitable, they don’t have to result in significant physical decline. By implementing these strategies—which emphasize strength training, a balanced diet, recovery, and mobility—you can cultivate a robust foundation for healthy aging. Embracing this new approach can lead to a healthier, more independent life as you move forward.
Image Source: Unsplash